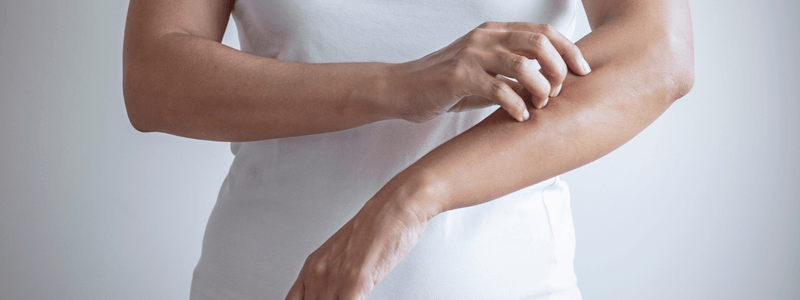
Sometimes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin may result from your diet. Itchy, irritated skin is caused by various things like food allergies, dry skin, and certain fabrics. You’ll find that eczema and food allergies often go hand in hand. For some people, merely touching or consuming certain foods results in contact dermatitis. When your skin is affected by something you’ve eaten, it might take hours or a few minutes for the symptoms to show. These symptoms may include redness alone or in combination with other symptoms like rash, swelling, or itchiness.
Even though many conditions may result in itchiness, food allergies and intolerances are at the top of the list. Sometimes itchiness may be due to a bug bite, sunburn, or dry skin. But we’ll look at the two common culprits that cause itching; food allergy and food intolerance.
Food allergy
According to researchers, about 2 to 5 percent of adults suffer from food allergies. Food allergies occur when your body reacts to specific proteins found in that food leading to a release of antibodies that cause an inflammatory effect. Because exposure to allergen foods causes such a reaction, you’ll notice symptoms like hives, swelling, flushing, and itchiness. These symptoms are the most common ones in the case of a food allergy. However, an allergic reaction can also include other symptoms affecting your heart, breathing, and digestion. Food allergy symptoms show up within minutes or even hours of consuming the trigger food. If you reckon you may be suffering from a food allergy, it is essential to take a home-lab Allergy Test to help you determine the foods your body is reacting towards.
Food intolerance

Our Intolerance 80 Test Kit.
Food intolerances are even more common than good allergies but less life-threatening. Food intolerances don’t affect the immune system like food allergies. Still, they affect the digestive tract, resulting in diarrhoea, bloating gas, and nausea. Besides these gastrointestinal symptoms, they can sometimes trigger itchiness. Even though food intolerances can’t cause life-threatening issues like anaphylaxis, they can still significantly impact your life. That’s why it’s necessary to get a home-lab Intolerance Test that will check for any food intolerances you may have to avoid in the future.
Common food intolerances that may cause itching
Food intolerances mainly cause digestive issues. But in some cases, it can also cause itchy skin. Here are some food groups that may cause itchiness in cases of food intolerance.
Sulfites
Some foods like grapes and aged cheese naturally contain sulfites. However, sulfites can also be added to beverages and foods to make them last longer. People sensitive to sulfites may experience hives, itchiness, skin rashes, abdominal pain, and diarrhoea. If you’re intolerant to sulfites, avoiding foods like wine, dried fruit, pickled foods, beer, and some baked goods is best.
Histamine-containing foods
When your body can’t break down histamines properly due to histamine intolerance, it can build up inside you, causing symptoms like hives, itching, headaches, and stomach cramps. If you’re dealing with histamine intolerance, a low histamine diet can help. You will also need to avoid foods like wine, fermented foods, dried fruit, certain cheeses, cured meats, vinegar, beer, and some fruits (dried and citrus).
Gluten
Gluten intolerance can cause gastrointestinal symptoms like diarrhoea, nausea, gas, bloating, and constipation. Amongst these symptoms, you’ll also find skin issues like itchiness, eczema, and psoriasis. If you’re gluten intolerant, you’ll need to stay away from foods containing gluten if you want to avoid such symptoms.
Foods that cause itching
Most of the time, you’ll find that foods causing itchiness do so due to food allergies. You’ll find rashes, redness, swelling, and itchy skin when you’re allergic to a particular food. Here are some common foods that cause itchiness when you have an allergy.
Milk
Milk allergies are prevalent in children, especially infants. You’ll find a child allergic to breast, cow, sheep, goat, and other mammal’s milk. Milk allergy triggers the immune system. The most common culprits are casein and whey; these proteins found in milk trigger the immune system to release antibodies that result in inflammation.
The most common milk allergy symptoms you’ll witness include hives, digestive problems, itching or tingling around the mouth, wheezing, vomiting, hives, and swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat. Certain allergy symptoms may take longer to manifest in babies, including loose stools, abdominal cramps, and colic. Milk allergy can be quite severe as it can result in life-threatening anaphylaxis and requires immediate medical attention. If you think you’re allergic to milk or your child is allergic, the best treatment is to avoid dairy products, including yoghurt, cheese, ice cream, and butter.
Eggs
Egg allergies are also common in children. However, around 70% of children outgrow this allergy. You’ll find that proteins in egg yolks or egg whites trigger allergy symptoms. The most common allergen proteins in egg whites include ovalbumin, ovotransferrin, egg white lysozyme, and ovomucin {1}. The main sign of egg allergy is hives which result in itchy, red, and swollen skin.
Egg allergy symptoms may also include gastrointestinal symptoms like vomiting, diarrhoea, and stomach pain. Also, most people with eczema find that eating eggs aggravates their condition. If you’re allergic to chicken eggs, avoid other types of eggs, including goose, duck, turkey, or quail unless you’ve spoken to your doctor.
Fish
Unlike egg and milk allergies, fish allergy mainly develops in adulthood. About 40% of people suffering from fish allergy report not having this issue until they were adults. Fish allergies are a result of an allergic reaction to finned fish like tuna, salmon, catfish, and cod. The most common protein in fish that causes an immune response is parvalbumins.
Symptoms of a fish allergy include skin rash, nausea, diarrhoea, headaches, stuffy nose/ congestion, hives, itching, and stomach pain. You may be allergic to certain fish and not others. But as a precaution, avoiding all types of fish is best.
Shellfish
The most common protein in shellfish that causes allergies is tropomyosin. If you have a shellfish allergy, you’ll be triggered by foods like shrimp, crab, lobster, squid, oysters, and scallops. Shellfish tend to have a hard exterior, and that’s how you differentiate them from other types of fish. Some people aren’t allergic to shellfish, while others are allergic to all types.
The most common shellfish allergy symptoms include hives, skin rashes, nausea, and itching. However, low blood pressure, wheezing, and even anaphylaxis can be fatal in severe cases. In such cases, one needs to have emergency medical help.
Wheat

An image of various type of wheats.
Even though we know wheat is in bread; it can also be in unsuspecting foods like soy sauce and hot dogs. Wheat allergy symptoms occur when your immune system detects wheat proteins like albumin, globulin, gliadin, and gluten. Wheat allergy is so common that it affects around 1% of the population on earth. According to research, wheat allergies are rampant in those who have asthma, seasonal allergies, and eczema.
Wheat allergy symptoms include itching, digestive distress, and respiratory problems. If you suffer from a wheat allergy, you must avoid foods containing wheat, including bread, couscous, bulgur, flour, pasta, crackers, farro, and farina. You will also need to carefully read labels because wheat can be found in salad dressings, sauces, soups, and processed meats.
Soy
Like milk and egg allergies, soy allergy mainly affects children even though some grow out of it. Soy can be found in baby formula and certain processed foods. Even though soy allergies primarily affect children, they also affect about 0.5% of the general population. So allergy results from a reaction to soy protein found in many soy-based products like miso, tofu, soybeans, edamame, and tempeh.
Soy allergies cause severe symptoms like swelling, tingling of the mouth, stomach pain, and wheezing, which require immediate medical help. In mild cases, you’ll observe symptoms like atopic dermatitis, which include itchy skin, especially on the face and mouth. When you have a soy allergy, avoiding all soy-based products and those with soy ingredients is necessary. However, you can safely consume refined soy oil and soy lecithin.
Peanuts
Peanuts are known for sending many people to the emergency room since they cause anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition requiring emergency medical treatment. You don’t need to eat peanuts to get allergy symptoms from it. It can result from cross-contamination from other foods or inhaling peanut dust or oil. According to research, having allergies may increase the risk of severe reactions in those with peanut allergies.
The most common peanut allergy symptoms include swelling under the skin, wheezing, shortness of breath, digestive issues, itching, hives, runny nose, and trouble breathing. Since peanut allergy can have such severe symptoms, it is safer to avoid all types of foods with peanuts as an ingredient and peanuts themselves.
Tree nuts
Similar to peanuts, tree nuts are also a common cause of anaphylaxis. You may get an allergic reaction from consuming tree nuts or nut-based oils, butter, flour, or milk. Tree nuts refer to any nuts that grow in trees. These include cashews, almonds, walnuts, pine nuts, pecans, pistachios, hazelnuts, and Brazil nuts. Around 25% to 40% of people with peanut allergies also suffer from at least one other nut allergy. Tree nut allergies are prevalent, affecting approximately 4.9% of the world’s population {2}.
The cause of allergies in tree nuts are often proteins like oleosins, legumin, vicilins, and 2S albumins found in these nuts. Common tree nut allergy symptoms include itchiness, tingling, skin redness, and mouth swelling. Those suffering from underlying conditions like asthma, eczema, and hay fever often suffer more severe reactions such as anaphylaxis. It is possible to suffer an allergy to certain tree nuts and not others. However, it is safer to avoid all of them because of the likelihood of cross-contamination.
Raw fruits and vegetables
Oral Allergy Syndrome (OAS) is adults’ most common type of food allergy. When you experience OAS, proteins found in raw foods or vegetables that you’re consuming contain proteins triggering your internal system. The most common symptom of OAS is itchiness in the mouth, face, or throat. However, this is mostly a mild reaction and won’t last if you rinse your mouth. You can also consume these foods after cooking them because the proteins will be cooked down and won’t cause any symptoms. You’ll mostly suffer from OAS after eating raw apples, celery, kiwi, peaches, plums, and carrots.
Tomatoes, spices, and citrus fruits
Often you’ll find that tomatoes trigger dermatitis in most individuals who are sensitive to Balsam of Peru. Balsam of Peru is the most prevalent allergen used in making fragrances, some medicines, and flavourings. If you’re sensitive to Balsam of Peru, other foods that may cause a reaction include chocolate, colas, and spices like cinnamon, vanilla, and cloves. If you’re allergic to Balsam of Peru, you’ll also need to avoid citrus fruits as it causes dermatitis flare-ups. Citrus include grapefruits, oranges, lemons, limes, cumquats, and mandarins.
Foods containing nickel
If you’re sensitive to nickel, then you need to avoid it in jewellery and watch bands and in foods. Foods that have high levels of nickel can result in skin symptoms like itchiness, redness, and swelling. Foods with high levels of nickel include beans, lentils, peas, soya beans, some canned foods, and grains like whole wheat bread and oatmeal.
Testing for food allergy and intolerance
Now that you know the relationship between itchiness and a food allergy and intolerance, you can determine which foods are causing you these symptoms and avoid them. However, we often mix different foods in our meals, which can get past us determining which one we should avoid as it triggers itchiness. However, you can get an Allergy and Intolerance Test to check which foods are causing itchiness and cut them off your diet. The only way to prevent itchiness after eating certain foods is by cutting them from your diet.
References
- Mathew, P., & Pfleghaar, J. L. (2019). Egg allergy.
- Geiselhart, S., Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K., & Bublin, M. (2018). Tree nut allergens. Molecular immunology, 100, 71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2018.03.011






